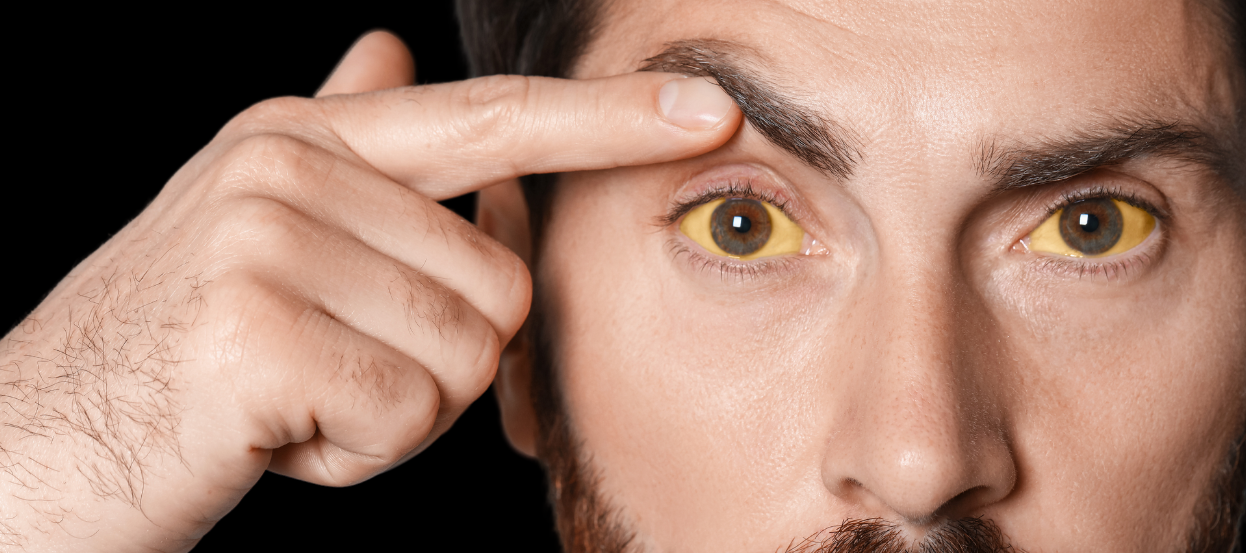
Yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes is known as jaundice. It happens due to excess deposition of bilirubin (yellowish pigment made during the breakdown of red blood cells) and It can happen with various health conditions and usually indicates a problem with the liver or bile ducts.
The liver removes bilirubin from the blood and deposits it in your stool. An accumulation known as hyperbilirubinemia, or jaundice, happens when your liver is overworked or when there is an excess of it in your system. This results in jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
Jaundice frequently affects newborns. In the first few days following delivery, about 60% of babies experience jaundice, commonly referred to as icterus. It is less frequent in adults, but they can still get it. If you suspect jaundice, get medical attention immediately. It might indicate an issue with the liver, blood, or gallbladder.
Jaundice, also known as hyperbilirubinemia, is a yellow discoloration of the body tissue resulting from the accumulation of an excess of bilirubin. Deposition of bilirubin happens only when there is an excess of bilirubin, a sign of increased production or impaired excretion. The normal serum levels of bilirubin are less than 1 mg/dl. However, the clinical manifestations of jaundice as scleral icterus (peripheral yellowing of the eye sclera), are best recognized only when the levels rise beyond 3 mg/dl.
There are three different types of Jaundice:
Usually, Jaundice results from an underlying illness that either makes the body produce too much bilirubin or keeps the liver from eliminating it. The following are the possible underlying conditions and causes of jaundice:
Jaundice may show no symptoms at all. The severity of your disease may determine any symptoms you experience. Scleral icterus, sometimes known as jaundice eyes, and skin yellowing are well-known symptoms. The other symptoms of jaundice include:
Typically, adults with jaundice don't receive treatment. However, the underlying condition will be treated by your doctor. As your liver heals, jaundice resulting from severe viral hepatitis will go away on its own. If the cause is a blocked bile duct, your physician might recommend opening it surgically. Your doctor may recommend taking cholestyramine orally if it is causing you discomfort. Your body produces bile acids, which itch. This medicine is used to get rid of them.
Depending on the severity, cholestasis-related pruritus can be treated. Warm baths or oatmeal baths might be soothing for mild cases of pruritus. Pruritus might also benefit from antihistamines. Colestipol or cholestyramine, two bile acid sequestrants, work for patients with moderate-to-severe pruritus. Sertraline, phenobarbital, rifampin, and naltrexone are among other less successful treatments. Liver transplantation can be the only viable treatment for pruritus if other medical options are exhausted.
For the treatment of jaundice in neonates, phototherapy is used. In phototherapy, bilirubin is broken down and expelled from the body through the use of bright white or blue-spectrum light. While phototherapy is used to treat jaundice in newborns, it has not been demonstrated to be useful in treating jaundice in adults.
A better prognosis or prevention for adult jaundice may also be possible with certain lifestyle modifications. These include:
Jaundice is characterized by yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and eye whites. This indicates a potential underlying medical ailment or liver-related issue. It happens when the liver becomes damaged or is unable to meet the body's need for processing waste products in the blood. Jaundice can be caused by a number of illnesses that affect the liver. Jaundice is usually treated by taking care of the underlying cause.
As soon as you discover any causes and symptoms of jaundice, visit Dr. Abhishek Yadav to get Jaundice treatment in Pune, India. He is one of the top liver specialist in Pune, India.
Q: Can sun exposure treat jaundice?
A: The bilirubin level may be lowered by exposing the baby to sunshine, but this will only be effective if the newborn is fully naked. It may not be safe to do this inside your house since your baby will get cold, and it is never a good idea to leave infants outside in the sun as they could burn.
Q: What happens if jaundice is not treated in adults?
A: If acute viral hepatitis is the cause of the jaundice, it may eventually go away on its own as the liver heals without the need for medication. Even if the jaundice goes away, hepatitis can nevertheless become chronic. Unlike in neonates (see Hyperbilirubinemia), adults with jaundice need not need therapy for the condition itself.
Q: How does the jaundice clear up?
A: Jaundice in adults is typically left untreated. However, the underlying medical ailment will be treated by your doctor. Jaundice caused by acute viral hepatitis will go away on its own as your liver recovers. Your doctor can advise surgery to open the bile duct if it is the cause of the problem.
Q: How long does jaundice take to resolve in children?
A: Jaundice in breastfed babies typically lasts one month, however, it can sometimes last longer. In formula-fed babies, most jaundice resolves in 2 weeks. Let your pediatrician know if your baby has jaundice for more than 2 weeks if your baby is formula-fed or longer than 4 weeks if your baby is primarily breastfed.