 Dr. Abhishek Yadav
Dr. Abhishek YadavThe liver and biliary tract were thought to be mystical organs with a complex anatomy, a vast array of functions, and remarkable regeneration potential for centuries. The treatment of hepatobiliary disease has undergone an enormous transformation in the last few decades. These advancements have largely been attributed to improved understanding of anatomy and physiology as well as a variety of newly developed diagnostic and therapeutic techniques. Surgery has played a key role in these developments. Such advances have led to the emergence of the specialty of hepato-pancreato-biliary surgery.
Hepato-pancreato-biliary (HPB) surgery encompasses general surgical management of diseases (both benign and malignant) of the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and bile ducts. These are some of the most complicated and challenging surgeries, requiring a high level of competence and skill with a multi-disciplinary approach.
The understanding regarding entirely novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for the treatment of hepatic-pancreatic-biliary (HPB) disease is expanding at a fast pace. With the use of the latest techniques, hepatic-pancreatic-biliary (HPB) disorders can be diagnosed more accurately and treated with resection, ablation, or other appropriate measures more prudently.
Schedule a call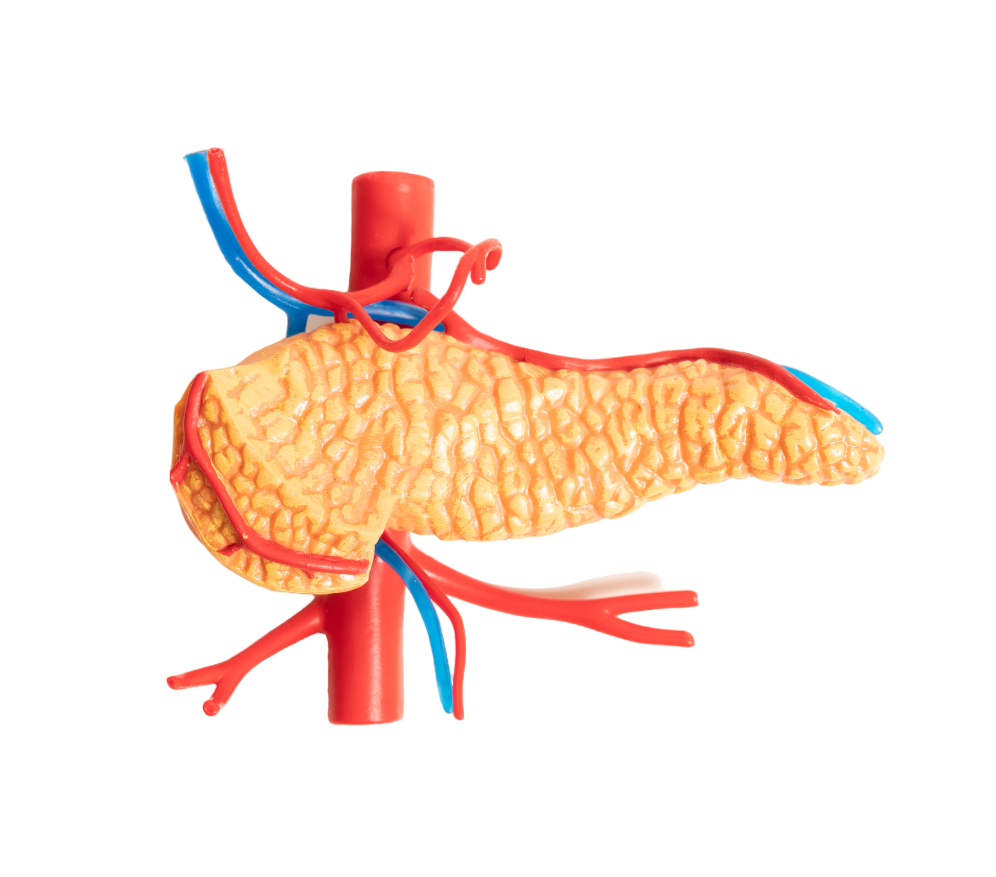
Get trustful insight about your liver problems and the accurate personalized treatment for it. Your well-being is important to us. Book your appointment for a second opinion.
Contact Us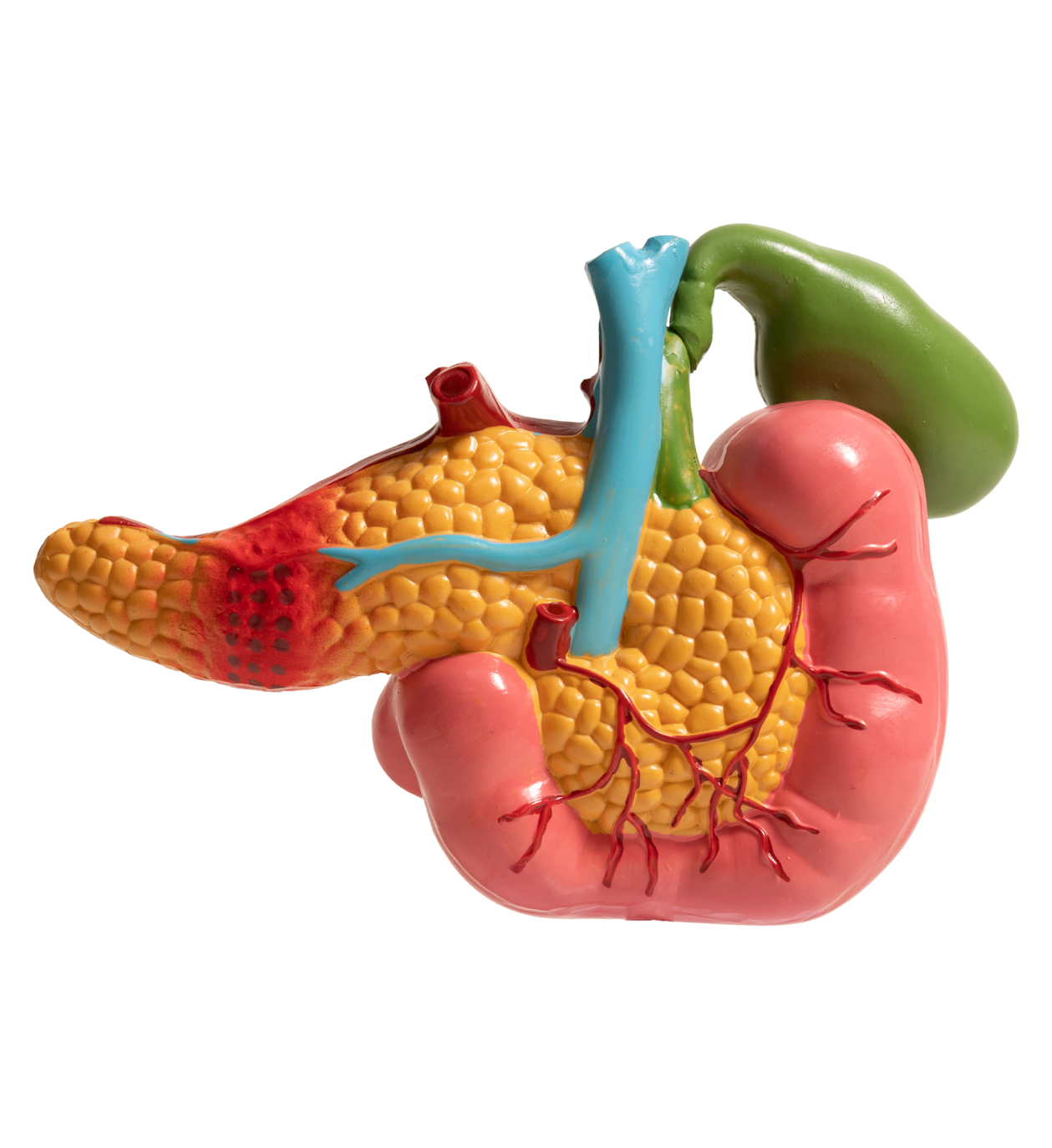
 Acute Hepatitis
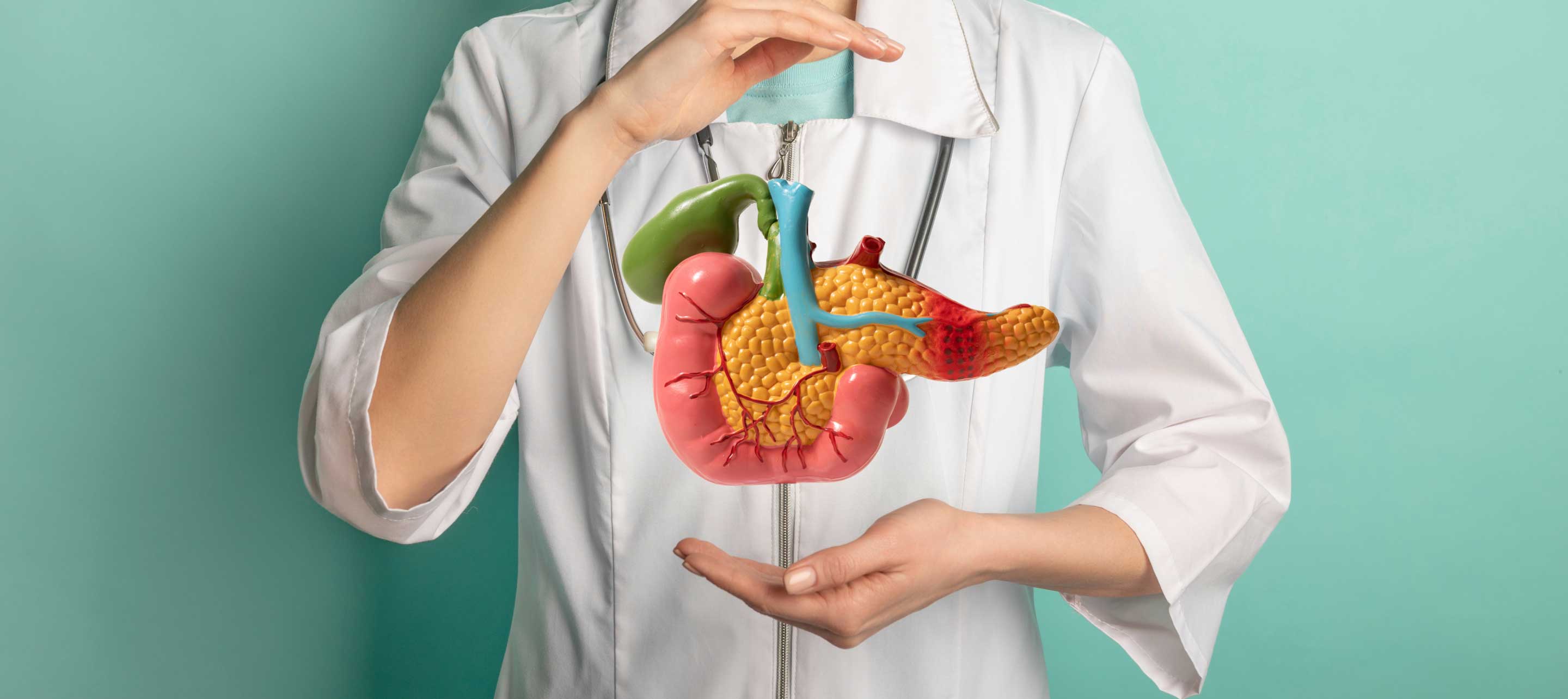
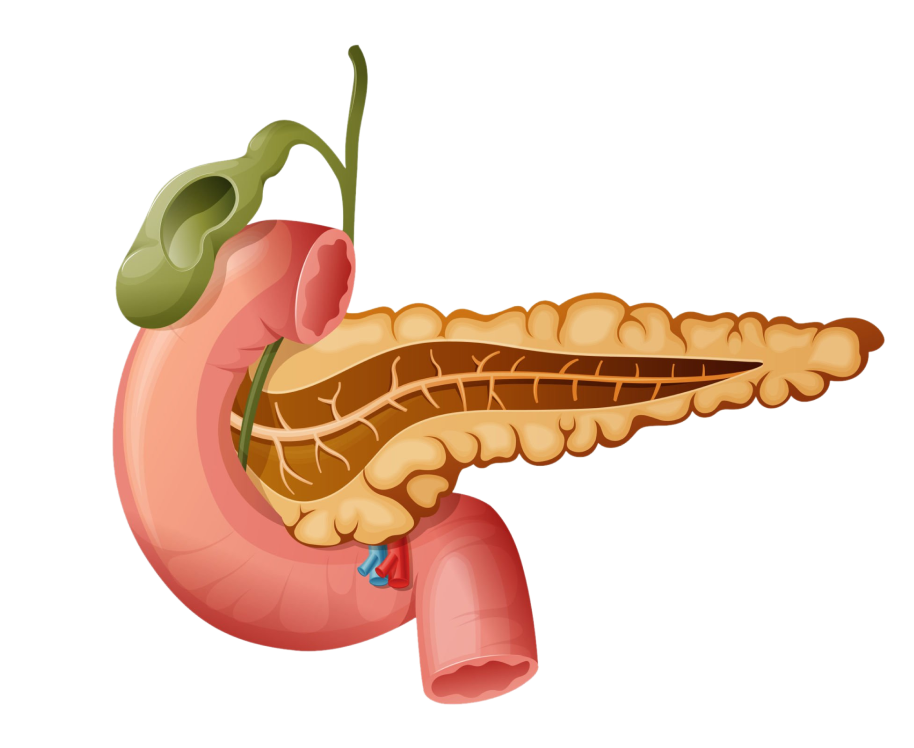
Acute HepatitisHepato refers to the liver, pancreato to the pancreas, and the gallbladder and bile ducts are part of the biliary system. Hepato-pancreato-biliary (HPB) disease is a general term for conditions affecting the liver, pancreas, or biliary tract. The prognosis for these intricately interconnected systems can range from manageable to critical, based upon the nature and stage of the ailment. Hepato-pancreato-biliary (HPB) surgery is a subspecialty of general surgery that treats diseases of the liver, pancreas, and biliary tract that can be benign or malignant.
HPB surgery helps in treating numerous conditions that fall under the category of HPB surgery. One of the most complex surgical techniques used in general surgery is HPB surgery. These essential organs depend heavily on a sophisticated network of blood vessels, including veins, to continue optimum functioning. Because of its complexity, surgeons must possess an exceptional level of competence and expertise to perform this surgery. It calls for a thorough comprehension of the complex vascular networks that are present in the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
 CONTACT US
CONTACT USFollowing are the diseases that can be treated with Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary (HPB) Surgery:
Diseases associated with liver:
Diseases associated with gallbladder:

Diseases associated with bile duct:
Diseases associated with Pancreas:
 CONTACT US
CONTACT USThe main method for possibly treating a variety of HPB conditions and providing patients with efficient treatment options is HPB surgery. While some procedures are complex and minimally invasive, others are more complicated. Every surgical procedure is unique and targets a particular aspect of conditions related to HPB. There are three main types of HPB surgery: laparoscopic, robotic, and open.
Like complicated gallbladder resections or major hepatic resections, are more complex surgeries. It involves wider incisions and complex therapeutic interventions.
Is an advanced medical technique that employs robotic systems to precisely and specifically execute surgical procedures. This technique is widely utilized in HPB procedures and has benefits like improved dexterity and less invasive incisions.
Another minimally invasive procedure is laparoscopic surgery. This kind of surgery executes a variety of surgical procedures using small cuts and specialized instruments equipped with cameras. This method, which offers advantages like less postoperative pain and faster recovery, is widely utilized in HPB surgeries.
The pre-evaluation procedure for Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary (HPB) surgery may involve thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history recording, and physical examination. Findings from these examinations, may call for the following investigations for reaching to a final diagnosis and chart-out the right treatment plan:
Following are the Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary (HPB) surgical approaches:
For Liver
For pancreas
For Bile Duct and Gallbladder
Following are the complications associated with this surgery:
There are numerous treatment options available to you if you or a loved one has been diagnosed with liver, pancreas, or biliary tract disease. Modern methods, such as Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary (HPB) Surgery, provide patients with new hopes and better quality of life. Most of the strategies in this surgery are patient-centered and aimed at promoting your recovery and long-term health. If you are suffering from diseases associated with liver, biliary ducts, and pancreas, reach out to the liver transplant and HPB surgeon in Lucknow and discuss the need and outcome of this surgery.
A: Because nerves were cut during the procedure, the skin surrounding the incision may remain numb and may improve with time. To fully recover, it might take you four to eight weeks.
A: Postoperative complications from hepatobiliary surgery include urinary tract infection, subphrenic infection, venous catheter-related infection, incisional infection, pulmonary atelectasis or infection, intraperitoneal hemorrhage, and gastrointestinal tract bleeding. These complications are also common to general abdominal surgery.
A: Surgical subspecialty hepato-pancreato-biliary (HPB) surgery, also called hepatobiliary surgery, focuses on treating diseases of the liver, pancreas, bile duct, and gallbladder, including cancer.
A: Major hepatic resection and pancreatic surgery are two procedures that are included in hepato-pancreatico-biliary (HPB) surgery; both are intricate and carry a high risk of complications.
A: Three to seven small incisions are made to remove the liver mass after the patient is put to sleep with general anesthesia. The process can take one to seven hours, depending on the lesions as well as the volume of liver that needs to be removed.