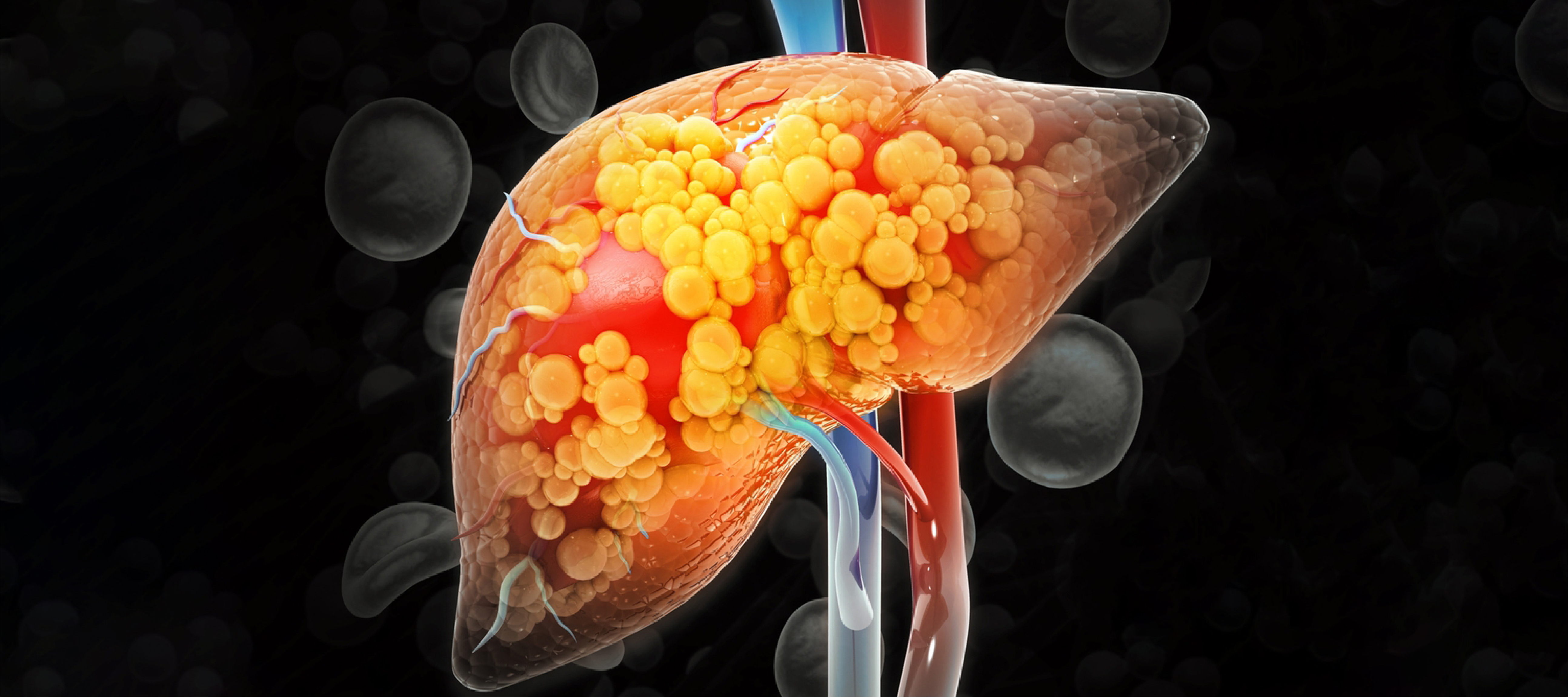
Fatty liver disease is a condition characterized by an excessive amount of fat in the liver, leading to inflammation and other associated illnesses.This condition affects detoxification, bile production, and vitamin storage.
This condition is increasing globally due to obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and substandard diets. Under normal circumstances, there is always some fat content in the liver, but when it increases to a level of more than 5-10% of the liver, then it is regarded as lethal.
Most cases are asymptomatic, and patients often wait until the disease progresses. This blog will give you an overview of fatty liver disease.
Understanding the disease's nature, symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments is crucial for managing it effectively.
There are two main types for fatty liver:
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is the most common form of fatty liver disease and is predominantly seen in developing nations and most of the developed nations in the world. It is found in people who rarely or do not drink alcohol at all, and its cause has not been determined. However, it is strongly related to metabolic risk factors, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance. NAFLD is mainly characterized by simple steatosis, also known as ‘fatty liver', to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is characterized by inflammation that leads to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even HCC.
AFLD is directly linked to alcoholism and taking too much alcohol as a drink. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver, so it stands to reason that continued intake of heavy quantities of alcohol can overwork any given liver to the point of fat generation. If left untreated, Alcoholoic Fatty Liver Disease can also escalate to more serious liver diseases, including alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis, the last of which is lethal.
The development of fatty liver problems is influenced by a combination of factors, many of which are related to lifestyle and metabolic health. The specific causes can vary depending on whether the condition is classified as NAFLD or AFLD:
Obesity:
One of the most significant risk factors for NAFLD is obesity, particularly when excess fat is stored around the abdomen (visceral fat). Obesity leads to increased fat deposition in the liver, promoting the development of fatty liver disease.
The risk of NAFLD is increased in people with type 2 diabetes.Insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes, is closely linked to the accumulation of fat in the liver. When the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, it can lead to increased fat storage in the liver.
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is often part of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and NAFLD. High blood pressure can contribute to liver damage and exacerbate the progression of fatty liver disease.
Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, along with low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, are common in individuals with NAFLD. Dyslipidemia (an abnormal amount of lipids in the blood) contributes to fat accumulation in the liver.
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to higher levels of glucose and fatty acids in the blood. This can result in increased fat deposition in the liver, contributing to the development of NAFLD.
The primary cause of AFLD is the consumption of large amounts of alcohol. Alcohol can directly damage liver cells and lead to fat accumulation, inflammation, and scarring (fibrosis).
Fatty liver disease is often referred to as a "silent" condition because it may not cause any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, some individuals may begin to experience symptoms that indicate liver dysfunction:
The treatment of fatty liver disease primarily focuses on addressing the underlying causes and preventing further liver damage. Here are some common strategies for managing fatty liver disease:
For individuals with NAFLD, weight loss is one of the most effective ways to reduce fat in the liver. Even a modest weight loss of 5–10% of body weight can significantly improve liver health and reduce the risk of progression to more severe liver disease. Weight loss should be achieved gradually through a combination of dietary changes and increased physical activity.
A fatty liver diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help improve liver function and reduce fat accumulation. It is also important to limit the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars, which can contribute to liver fat buildup.
Engaging in regular physical activity can help with weight loss and improve overall metabolic health. Exercise can reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower the risk of developing more severe liver conditions.
Avoiding alcohol is crucial for those with AFLD in order to avoid further liver damage. Even for those with NAFLD, avoiding alcohol can be beneficial, as alcohol can further increase liver inflammation.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions that contribute to this condition, such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure.
Regular monitoring of liver function and overall health is important. This may involve periodic blood tests, imaging studies, and consultations with a healthcare provider to assess the liver's condition and adjust treatment as needed.
Steatohepatitis is not a rare disease; however, its diagnosis in most cases does not take place, and the disease in the absence of proper treatment can lead to decompensation. It is vital to know what causes this, how to identify its signs and change the approach to its treatment, hence the goal of managing this condition. Diet and sexual behaviors like obesity, excessive eating, sedentary living, and excessive alcohol are among the prime causes of FLD and help to reverse it by undertaking minor changes in that behavior. If you think that you may belong to this group, it is best to consult your doctor and have yourself professionally checked and advised.